- Dorsal anatomy
- Ventral anatomy
- Lateral anatomy
- Male vs. Female
- Brachypterous vs. Macropterous
- Life stages of the young soapberry bug
- Nymph vs. Adult
- Beak length vs. Fruit radius
- General terms
Dorsal anatomy
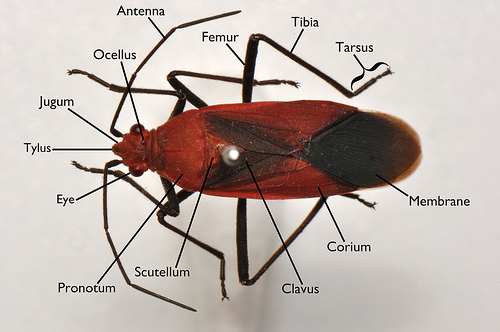
- Clavus: part of the forewing that surrounds the scutellum when the wings are folded
- Corium: hardened part of forewing; does not include the clavus
- Jugum: lobe on tip of head; there is one on either side of the tylus
- Membrane: translucent tip of forewing
- Ocellus: simple eye that is found on the top of the head ("simple" because it only contains a single lens)
- Pronotum: dorsal plate that covers the thorax
- Scutellum: triangular plate that lies behind the pronotum
- Tylus: tip of the head that lies between the juga
Ventral anatomy
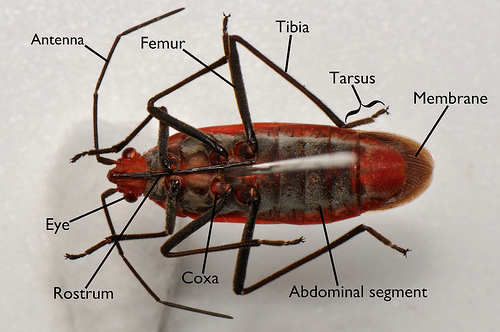
- Coxa: rounded segment of the leg that is closest to the body
- Rostrum: sheath that encloses the mouthparts; has four segments (also known as the beak or labium)
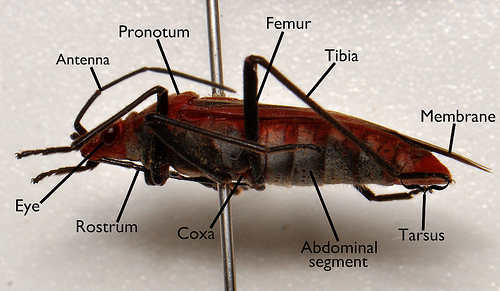
Lateral anatomy
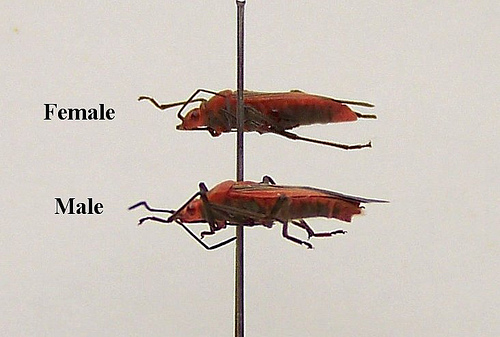
Male vs. Female
Brachypterous vs. Macropterous

- Brachypterous: short-winged; always incapable of flight
- Macropterous: long-winged; typically capable of flight (depends on state of flight muscles)
Life stages of the young soapberry bug
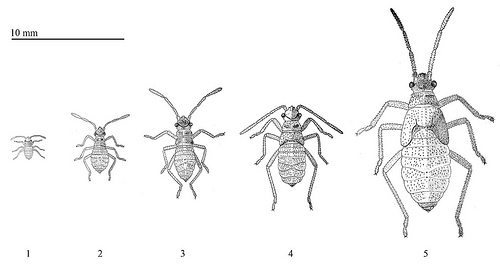
Nymph vs. Adult
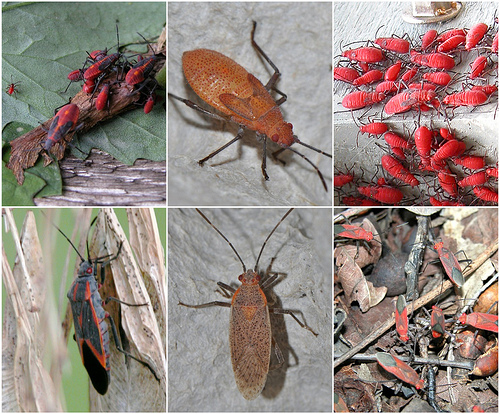

Columns from left to right: Boisea trivittata, Jadera coturnix, and Leptocoris vicinus
Beak length vs. Fruit radius
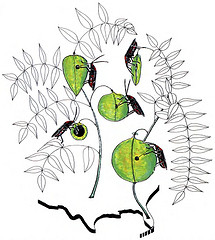
Host races of the soapberry bug species Jadera haematoloma are shown feeding on their phylogenetic trees (somewhat stylized). Their beaks extend through the fruits of each of five sapindaceous host species to feed on the seeds within. The southern border of the U.S. is at the bottom of the illustration.
Trees emerge from two regions: the southcentral states and Florida. For each tree, fruits of the native hosts are depicted nearest the base whereas fruits of the invasive host plants are connected as higher points. The host races of the soapberry bug have differentiated in beak length (depicted in this illustration) as well as several other morphological, behavioral, and life history characteristics (see link below for more information). Most of the host-selected differentiation on newly introduced host species has occurred in the past few decades.
-Adapted from Carroll and Boyd 1992
General terms
- Hemelytra: the partially hardened, partially membranous wings of Heteropterans
- Instar: the developmental stage between molts; they are often numbered (e.g. first instar, second instar, etc.); soapberry bugs exhibit five instars prior to adulthood
- Molt: shedding the exoskeleton to permit growth (for soapberry bugs, only nymphs do this)
- Nymph: an immature insect that has not yet reached adulthood
- Wing pads: the incomplete wing structures present on nymphs (not to be confused with the short wings of a brachypterous adult)


